Engineered antibodies and their fragments are invaluable instruments for an enormous vary of biotechnological and pharmaceutical purposes. However, they’re going through growing competitors from a new generation of protein display scaffolds, particularly chosen for binding just about any goal. Some of them have already entered medical trials.
Most of these nonimmunoglobulin proteins are concerned in pure binding occasions and have amazingly various origins, frameworks, and capabilities, together with even intrinsic enzyme exercise.
In many respects, they’re superior over antibody-derived affinity molecules and provide an ever-extending arsenal of instruments for, e.g., affinity purification, protein microarray expertise, bioimaging, enzyme inhibition, and potential drug supply.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”array” header=”2″ limit=”14″ start=”4″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
As wonderful supporting frameworks for the presentation of polypeptide libraries, they are often subjected to highly effective in vitro or in vivo choice and evolution methods, enabling the isolation of high-affinity binding reagents.
This article evaluations the generation of these novel binding reagents, describing validated and superior different scaffolds in addition to the latest nonimmunoglobulin libraries.
Characteristics of these protein scaffolds in phrases of structural stability, tolerance to a number of substitutions, ease of expression, and subsequent purposes as particular focusing on molecules are mentioned.
Furthermore, this evaluation exhibits the shut linkage between these novel protein instruments and the continuously growing display, choice, and evolution methods utilizing phage display, ribosome display, mRNA display, cell floor display, or IVC (in vitro compartmentalization).
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”ribosome” header=”2″ limit=”12″ start=”4″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
Here, we predict the vital function of these novel binding reagents as a toolkit for biotechnological and biomedical purposes.
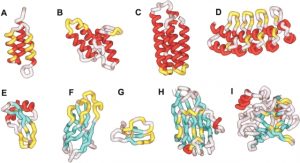
A new generation of protein display scaffolds for molecular recognition.
Recombinant Aspergillus fumigatus allergens: from the nucleotide sequences to medical purposes.
Members of the genus Aspergillus are opportunistic pathogens for cold- and warm-blooded animals. They are related to a formidable spectrum of illnesses in people, starting from benign colonization of the lung to life-threatening illnesses akin to invasive aspergillosis or allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA). Aspergillus fumigatus is the etiological agent recognized in most of the Aspergillus-related human illnesses and is subsequently of explicit medical relevance.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”aspergillus” header=”1″ limit=”22″ start=”4″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
A main drawback within the analysis of A. fumigatus-related problems arises from the shortage of standardized fungal extracts.
The allergenicity of business A. fumigatus extracts is dependent upon many elements together with the pressure used, progress circumstances, harvesting and extraction procedures hampering the event of diagnostic reagents appropriate for the discrimination between A. fumigatus-related illnesses.
Molecular DNA/RNA applied sciences and biotechnological procedures enable cloning, characterization and manufacturing of giant quantities of single, extremely pure allergens. The growth of phage floor display applied sciences for cloning cDNAs has accelerated the isolation of candidate cDNAs encoding allergens.
Screening of an A. fumigatus cDNA library displayed on the floor of phage M13 allowed characterization and manufacturing of a panel of allergens recognized as proteins with identified organic perform or as allergens with out sequence homology to identified proteins. They belong to 2 practical classes: secreted and cytoplasmic proteins. Secreted allergens are acknowledged by serum IgE of A.
fumigatus-sensitized people with or with out ABPA, whereas nonsecreted allergens are solely acknowledged by serum IgE of ABPA sufferers. The dissection of IgE-mediated immune responses to single A.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”igE” header=”2″ limit=”22″ start=”4″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
fumigatus allergens permits a discrimination between ABPA and A. fumigatus sensitization with excessive specificity and sensitivity demonstrating the facility of recombinant allergens for the differential analysis of A. fumigatus-related pulmonary problems.