Bacterial pathogens have developed particular effector proteins that, by interfacing with host kinase signalling pathways, present a mechanism to evade immune responses throughout an infection.
Although these effectors contribute to pathogen virulence, we realized that they may additionally serve as worthwhile artificial biology reagents for engineering mobile behaviour.
Here we exploit two effector proteins, the Shigella flexneri OspF protein and Yersinia pestis YopH protein, to rewire kinase-mediated responses systematically each in yeast and mammalian immune cells.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”Yersinia” header=”2″ limit=”11″ start=”4″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
Bacterial effector proteins could be directed to inhibit particular mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways selectively in yeast by artificially concentrating on them to pathway-specific complexes.
Moreover, we present that distinctive properties of the effectors generate new pathway behaviours: OspF, which irreversibly inactivates mitogen-activated protein kinases, was used to assemble an artificial suggestions circuit that exhibits novel frequency-dependent enter filtering.
Finally, we present that effectors can be utilized in T cells, both as suggestions modulators to tune the T-cell response amplitude exactly, or as an inducible pause swap that may briefly disable T-cell activation.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”tcell” header=”2″ limit=”14″ start=”4″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
These research exhibit how pathogens may present a wealthy toolkit of components to engineer cells for therapeutic or biotechnological purposes.
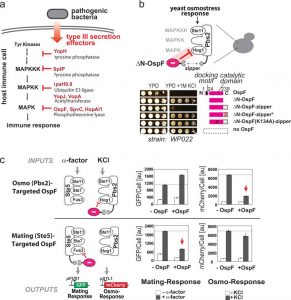
Bacterial virulence proteins as tools to rewire kinase pathways in yeast and immune cells.
Potential purposes of enzymes immobilized on/in nano supplies: A evaluate.
Several new varieties of carriers and applied sciences have been carried out in the current previous to enhance conventional enzyme immobilization which aimed to improve enzyme loading, exercise and stability to lower the enzyme biocatalyst price in industrial biotechnology.
These embody cross-linked enzyme aggregates, microwave-assisted immobilization, click on chemistry know-how, mesoporous helps and most just lately nanoparticle-based immobilization of enzymes.
The union of the precise bodily, chemical, optical and electrical properties of nanoparticles with the precise recognition or catalytic properties of biomolecules has led to their look in myriad novel biotechnological purposes.
They have been utilized time and once more for immobilization of industrially necessary enzymes with improved traits.
The excessive surface-to-volume ratio supplied by nanoparticles resulted in the focus of the immobilized entity being significantly greater than that afforded by experimental protocols primarily based on immobilization on planar 2-D surfaces.
Enzymes immobilized on nanoparticles confirmed a broader working pH and temperature vary and greater thermal stability than the native enzymes.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”nanoparticle” header=”2″ limit=”17″ start=”4″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
Compared with the traditional immobilization strategies, nanoparticle primarily based immobilization served three necessary options; (i) nano-enzyme particles are straightforward to synthesize in excessive strong content material with out utilizing surfactants and poisonous reagents, (ii) homogeneous and nicely outlined core-shell nanoparticles with a thick enzyme shell could be obtained, and (iii) particle measurement could be conveniently tailor-made inside utility limits.
In addition, with the rising consideration paid to cascade enzymatic response and in vitro artificial biology, it’s doable that co-immobilization of multi-enzymes could possibly be achieved on these nanoparticles.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”enzymatic” header=”2″ limit=”15″ start=”4″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]