The butanol extract of <i>Asparagus cochinchinensis</i> roots fermented with <i>Weissella cibaria</i> (BAW) successfully prevents irritation and transforming of airway within the ovalbumin (OVA)-induced bronchial asthma mannequin. To characterize biomarkers that may predict the anti-asthmatic results induced by BAW therapy, we measured the alteration of endogenous metabolites within the serum of OVA-induced bronchial asthma mice after administration of low focus BAW (BAWLo, 250 mg/kg) and excessive focus BAW (BAWHi, 500 mg/kg) utilizing <sup>1</sup>H nuclear magnetic resonance (<sup>1</sup>H-NMR) spectral knowledge. The variety of immune cells and serum focus of IgE in addition to thickness of the respiratory epithelium and infiltration of inflammatory cells within the airway considerably recovered within the OVA+BAW handled group as in comparison with the OVA+Vehicle handled group.
In the metabolic profile evaluation, the sample recognition confirmed utterly separate clustering of serum evaluation parameters between the OVA+Vehicle and OVA+BAW handled teams. Of the overall endogenous metabolites, 19 metabolites had been upregulated or downregulated within the OVA+Vehicle handled group as in comparison with the Control handled group. However, solely four amino acids (alanine, glycine, methionine and tryptophan) had been considerably recovered after BAWLo and BAWHi therapy. This research offers the primary outcomes pertaining to metabolic modifications within the bronchial asthma mannequin mice handled with OVA+BAW. Additionally, these findings present that four metabolites can be utilized as one in all biomarkers to foretell the anti-asthmatic results.
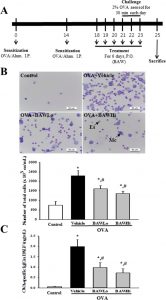
Four amino acids as serum biomarkers for anti-asthma effects in the ovalbumin-induced asthma mouse model treated with extract of Asparagus cochinchinensis.
Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors block the anti-nociceptive results of opioids in mouse chemotherapy-induced neuropathy and most cancers bone ache fashions.
Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is a ubiquitous sign transduction regulator, and Hsp90 inhibitors are in scientific growth as most cancers therapeutics. However, there have been only a few research on the impression of Hsp90 inhibitors on ache or analgesia, a severe concern for most cancers sufferers. We beforehand discovered that Hsp90 inhibitors injected into the mind block opioid-induced anti-nociception in tail flick, paw incision, and HIV neuropathy ache. This research prolonged from that preliminary work to check the cancer-related scientific impression of Hsp90 inhibitors on opioid anti-nociception in cancer-induced bone ache (CIBP) in feminine BALB/c mice and chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) in female and male CD-1 mice.
Mice had been handled with Hsp90 inhibitors (17-AAG, KU-32) by the intracerebroventricular, intrathecal, or intraperitoneal routes, and after 24 hours ache behaviors had been evaluated following analgesic drug therapy. Hsp90 inhibition within the mind or systemically utterly blocked morphine and oxymorphone anti-nociception in CIPN; this impact was partly mediated by decreased ERK and JNK MAPK activation and by elevated protein translation, was not altered by persistent therapy, and Hsp90 inhibition had no impact on gabapentin anti-nociception. We additionally discovered that the Hsp90 isoform Hsp90α and the co-chaperone Cdc37 had been accountable for the noticed modifications in opioid anti-nociception. In distinction, Hsp90 inhibition within the spinal twine or systemically partially lowered opioid anti-nociception in CIBP. These outcomes display that Hsp90 inhibitors block opioid anti-nociception in cancer-related ache, suggesting that Hsp90 inhibitors for most cancers remedy may lower opioid therapy efficacy.
Combined antitumor results of anti-EGFR variant III CAR-T cell remedy and PD-1 checkpoint blockade on glioblastoma in mouse mannequin.
Glioblastoma is without doubt one of the deadliest cancers. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell remedy in opposition to stable tumors has been removed from passable largely as a result of immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, resembling PD-1 mediated T cell exhaustion. In the current research, we investigated the mixed antitumor results of anti-EGFR variant III CAR-T cell remedy and PD-1 checkpoint blockade on glioblastoma in mouse mannequin. The outcomes demonstrated that CAR-T cells with PD-1 blockade exhibit increased killing effectivity in vitro.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”103-M463″ header=”5″ limit=”120″ start=”1″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
Additionally, CAR-T cells with PD-1 blockade confirmed simpler and protracted therapeutic results on glioblastoma and led to considerably elevated variety of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) within the mouse mannequin. In conclusion, PD-1 checkpoint blockade considerably enhanced the antitumor exercise of anti-human EGFRvIII CAR-T cells by overcoming TILs exhaustion.
