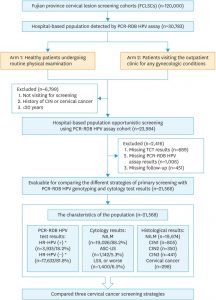
To consider the polymerase chain response (PCR)-reverse-dot-blot (RDB) human papillomavirus (HPV) genotyping test as a possible assay for the cervical cancer primary screening.In a hospital-based cohort, a complete of 21,568 ladies have been voluntarily enrolled from March 2009 to November 2016 for evaluating the three present cervical cancer screening methods: co-test, cytology primary and high-risk HPV (HR-HPV) primary through the use of PCR-RDB HPV genotyping and liquid-based cytology (thinprep cytologic test [TCT]).
Women with HR-HPV an infection and/or irregular cytology have been referred for colposcopy, and the biopsy or conization was carried out in line with the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology (ASCCP) tips.Overall, 18.20% (3,935/21,568) of the ladies have been detected as HR-HPV-positive, 5.04% (1,088/21,568) have been recognized with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 or greater (CIN2+), and three.43% (739/21,568) with CIN3+.
The cumulative incidence charges for CIN2+/CIN3+ in sufferers with HPV-16/18-positive have been 48.28%/37.20%, whereas they have been 0.86%/0.38%, 0.30%/0.15% and 0.18%/0.09% in cytology-negative, HR-HPV-negative and co-test-negative inhabitants, respectively. Using CIN2+ and CIN3+ as the noticed endpoints, the sensitivity and adverse predictive worth (NPV) of HR-HPV genotyping as a primary screening instrument have been 90.99%/99.49% and 91.57%/99.80%. Moreover, utilizing HR-HPV genotyping primary screening may detect the identical extra CIN2+/CIN3+ instances in baseline-detection as co-testing (990/700 vs. 991/701) and way over cytology primary screening (903/656, p<0.05).
It additionally achieved the bottom misdiagnosis price (8.01%/5.02%). Although HPV genotyping primary screening required an elevated variety of colposcopies (2.75/3.89 per CIN2+/CIN3+ case), it yielded an appropriate price.The PCR-RDB HPV genotyping test is a cost-effective and useful cervical cancer primary screening for hospital-based opportunistic screening.
PCR-reverse dot blot human papillomavirus genotyping as a primary screening test for cervical cancer in a hospital-based cohort.
Evaluation of dot-blottest for serological prognosis of bovine brucellosis.
The goal of this examine was to standardize and validate the dot-blot test for the serological prognosis of bovine brucellosis, evaluate the outcomes with these discovered in the 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME) and complement fixation test (CF), and estimate the relative sensitivity and specificity of the dot-blot in comparison with these assessments. Fifty bovine blood serum samples have been used for the test standardization, and 1315 samples have been used for analysis and comparability between the assessments; the outcomes have been in contrast utilizing the Kappa indicator.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”RW-401-D” header=”4″ limit=”155″ start=”3″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
At the top of standardization, it was established as optimum for the antigen obtained from Brucella abortus B19 after passing via a microorganism rupture course of, the blood serum samples diluted at 1:100, and the conjugate at 1:30,000. The comparability of the dot-blot outcomes with 2-ME confirmed Kappa index of 0.9939, sensitivity of 99.48%, and specificity 99.91%, with CF, Kappa index of 0.8226, sensitivity 100% and specificity 95.32%. Using the mix of the test outcomes 2-ME and CF to ascertain the true situation of the animal, the dot-blot confirmed relative sensitivity of 100%, and relative specificity of 99.91%. The evaluated test proved to be efficient and dependable, in addition to being simple to deal with and interpret the outcomes.