Aromatase inhibitors have been broadly used for the endocrine therapy of estrogen-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal sufferers. However, clinicopathological research of aromatase have been restricted due to unsatisfactory specificity and/or restricted availability of anti-aromatase antibodies. Here, we have now generated a polyclonal antiserum with high affinity and specificity for human aromatase utilizing a monoclonal antibody tagged immunoaffinity chromatography on an industrial manufacturing scale. Our preliminary immunohistochemical evaluation of 221 invasive breast cancer instances indicated that 87.3% (193/221) had at the very least 5% aromatase constructive cells. The histoscore for aromatase was inversely correlated with pT (p = 0.019), pN (p = 0.001), stage (p < 0.001), histologic grade (p = 0.003), lymphatic infiltration (p < 0.001), venous infiltration (p < 0.001), and Ki-67 index (p < 0.001).
However, cancer aromatase expression was impartial of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR), and human epidermal progress issue receptor 2 statuses. This antiserum will likely be relevant to clinicopathological examination of aromatase as well as to ER and PgR for an acceptable use of aromatase inhibitor on the therapy of breast cancer. Further research on the connection between Aromatase inhibitors have been broadly used for the endocrine therapy of estrogen-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal sufferers. However, clinicopathological research of aromatase have been restricted due to unsatisfactory specificity and/or restricted availability of anti-aromatase antibodies. Here, we have now generated a polyclonal antiserum with high affinity and specificity for human aromatase utilizing a monoclonal antibody tagged immunoaffinity chromatography on an industrial manufacturing scale. Our preliminary immunohistochemical evaluation of 221 invasive breast cancer instances indicated that 87.3% (193/221) had at the very least 5% aromatase constructive cells.
The histoscore for aromatase was inversely correlated with pT (p = 0.019), pN (p = 0.001), stage (p < 0.001), histologic grade (p = 0.003), lymphatic infiltration (p < 0.001), venous infiltration (p < 0.001), and Ki-67 index (p < 0.001). However, cancer aromatase expression was impartial of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR), and human epidermal progress issue receptor 2 statuses. This antiserum will likely be relevant to clinicopathological examination of aromatase as well as to ER and PgR for an acceptable use of aromatase inhibitor on the therapy of breast cancer. Further research on the connection between aromatase expression and aromatase inhibitors are warranted.
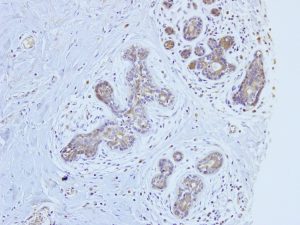
Preparation of a novel antiserum to aromatase with high affinity and specificity: Its clinicopathological significance on breast cancer tissue.