In our earlier research, utilizing a B cell vaccine (scFv-Her2), the concentrating on of tumor-associated antigen Her2 (human epidermal progress issue receptor-2) to B cells by way of the anti-CD19 single chain variable fragment (scFv) was proven to enhance tumor-specific immunity, which enhanced tumor management in the prophylactic and therapeutic setting. However, the fusion protein displayed restricted exercise in opposition to established tumors, and native relapses usually occurred following scFv-Her2 remedy, indicating that scFv-Her2-induced responses are insufficient to take care of anti-tumor immunity.
In this research, concentrating on the IV area (D4) of the extracellular area of Her2 to B cells by way of CD19 molecules (scFv-Her2D4) was discovered to reinforce IFN-γ-producing-CD8+ T cell infiltration in tumor tissues and decreased the variety of tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). However, adverse co-stimulatory molecules comparable to programmed cell loss of life protein-1 (PD-1), CD160, and LAG-Three on T cells and programmed loss of life protein ligand-1 (PD-L1) on tumor cells have been upregulated in the tumor microenvironment after scFv-Her2D4 remedy. Further, anti-PD1 administration enhanced the efficacy of scFv-Her2D4 and anti-tumor immunity, as evidenced by the reversal of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cell exhaustion and the discount of MDSCs and Treg cells, which suppress T cells and alter the tumor immune microenvironment.
Moreover, combining this with anti-PD1 antibodies promoted full tumor rejection. Our knowledge present proof of an in depth interplay amongst tumor vaccines, T cells, and the PD-L1/PD-1 axis and set up a foundation for the rational design of mixture remedy with immune modulators and tumor vaccine remedy.
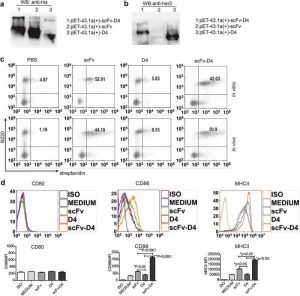
CD19-targeting fusion protein combined with PD1 antibody enhances anti-tumor immunity in mouse models.
Anti-inflammatory, analgesic exercise, and toxicity of Pituranthos scoparius stem extract: An ethnopharmacological research in rat and mouse fashions.
<AbstractText>Pituranthos scoparius is a medicinal plant that’s used in conventional drugs in Algeria and different North African nations to deal with a number of illnesses comparable to bronchial asthma, rheumatism, measles, dermatoses, jaundice, and digestive problems.</AbstractText><AbstractText>The current investigation was designed to research an ethnobotanical survey about Pituranthos scoparius in Setif area, Algeria, and assess the acute toxicity, in vivo anti-inflammatory potential and analgesic impact of Pituranthos scoparius stem h widespread drugs.</AbstractText><p><div><b>MATERIALS AND METHODS</b></div>Acute toxicity of PSSE was carried out primarily based on OECD pointers 425.
Both potential loss of life and indicators accompanying toxicity of animals have been monitored for 14 days to determine the median deadly dose (LD<sub>50</sub>) of PSSE. Anti-inflammatory impact of the extract was evaluated utilizing the xylene, croton oil-induced ear edema, and carrageenan-induced paw edema, whereas the analgesic exercise was evaluated utilizing acetic acid-induced stomach constriction in mice mannequin.</p><p><div><b>RESULTS</b></div>Data from the ethnopharmacological survey confirmed that 24.47% of individuals used this plant in conventional (people) drugs Results additionally revealed that PSSE comprises excessive quantities of polyphenols, flavonoids, and tannins, and that the extract didn’t trigger any deaths or adjustments in the conduct of handled animals; LD<sub>50</sub> values have been discovered to be greater than 5 g/kg DW.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”CD19″ header=”3″ limit=”120″ start=”1″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]
Additionally, no important variations have been noticed in the alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) enzymes, or in the degrees of urea and creatinine. Oral administration of PSSE on the doses of 100, 300, and 600 mg/kg produced a big dose-dependent inhibition impact in each xylene and croton oil-induced ear edema in mice. Administration of PSSE at a dose of 100, 250, and 500 mg/kg considerably (P ˂ 0.05) exhibited anti-edematogenic impact in the carrageenan-induced rat paw edema after Three h.
